Period Calculator: Accurately Predict Your Next Period Dates
Understanding your menstrual cycle is key to maintaining reproductive health and planning for pregnancy or period management. Our comprehensive menstrual cycle calculator goes beyond basic period prediction to give you detailed insights about your fertility, ovulation, and cycle phases. Whether you’re trying to conceive, monitor your health, or simply be prepared, this tool provides valuable information about your unique cycle patterns.
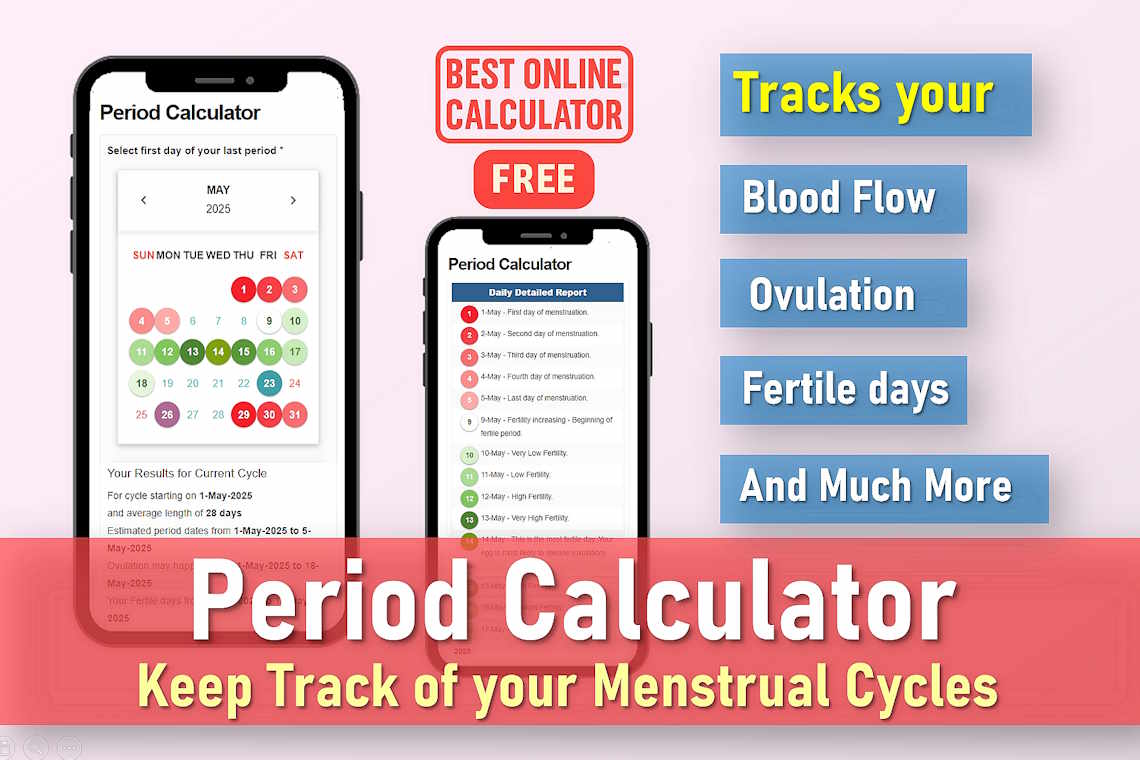
Select first day of your last period *
Related Calculators
How this Period Calculator Works
This advanced period tracking calculator delivers comprehensive insights across multiple aspects of your menstrual cycle:
- Period prediction: Estimates your next period start and end dates based on your cycle history
- Fertility tracking: Identifies your most fertile days and likely ovulation window
- Cycle phase analysis: Breaks down your follicular (pre-ovulation) and luteal (post-ovulation) phases
- Long-term planning: Projects your next six menstrual cycles for better preparation
- Daily insights: Provides a day-by-day fertility report with key biological events
- Health monitoring: Helps identify potential irregularities in your cycle length or symptoms
How to Use the Period Calculator Effectively
For the most accurate results, follow these steps carefully:
- First day of your last period: Enter the exact date when your most recent menstrual bleeding began (not spotting). This is considered Day 1 of your cycle.
- Period duration: Input how many days your bleeding typically lasts. Most women bleed for 3-5 days, but anywhere from 2-7 days is considered normal.
- Average cycle length: Calculate this by counting the days from Day 1 of one period to Day 1 of the next period. Track 3-4 cycles and average them for best accuracy.
Pro Tip: For irregular cycles, track your periods for at least 3 months to identify patterns and use the average cycle and period lengths for better results.
Understanding Your Period Calculator Results
1. Current Cycle Analysis
This section breaks down your current menstrual cycle into key components:
- Period dates: The estimated window when you can expect menstrual bleeding
- Ovulation window: The 5-7 day period when ovulation is most likely to occur (typically days 12-16 in a 28-day cycle)
- Fertile days: The optimal time for conception, which includes the 5 days before ovulation and the ovulation day itself
- Cycle phases:
- Follicular phase: From period start to ovulation (can vary in length)
- Luteal phase: From ovulation to next period (typically 12-16 days)
2. Future Period Projections
The calculator provides estimated dates for your next six menstrual cycles, allowing you to:
- Plan vacations or special events around your period
- Prepare for potential PMS symptoms
- Track long-term cycle patterns for health monitoring
- Identify gradual changes in cycle length over time
3. Detailed Daily Report
This day-by-day analysis helps you understand what’s happening in your body:
- Menstruation days: When you can expect bleeding and typical flow patterns
- Fertility levels: Rates your fertility potential from very low to peak
- Ovulation day: The most likely day for egg release (highest pregnancy chance)
- Implantation window: If conception occurs, when the embryo might implant
- Pregnancy test timing: Earliest date when a test might show positive results
Important Notes About Cycle Predictions
While our calculator uses scientific methods to estimate your cycle, many factors can influence your actual menstrual rhythm:
- Physical factors: Weight changes, intense exercise, or illness
- Hormonal influences: Birth control, breastfeeding, or perimenopause
- Health conditions: PCOS, thyroid disorders, or endometriosis
- Lifestyle factors: Stress, travel, or significant diet changes
Medical Disclaimer: This tool is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for concerns about irregular cycles, unusual symptoms, or family planning.
Additional Tips for Cycle Tracking
- Consider tracking basal body temperature for more accurate ovulation detection
- Monitor cervical mucus changes throughout your cycle
- Record PMS symptoms to identify patterns
- Note any spotting between periods
- Track sexual activity if trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy
Remember that every woman’s cycle is unique. What’s normal for you might differ from averages. Regular tracking over several months will help you understand your personal patterns and identify any changes that warrant medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s Considered a Normal Menstrual Cycle?
The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but it’s normal for cycles to range between 21 and 35 days. A typical period lasts between 2 to 7 days. Tracking your cycle over time helps determine what’s normal for you, as every body is different.
How Long Does a Normal Period Last?
A typical menstrual period lasts between 2 to 7 days. Most people bleed the heaviest during the first 2–3 days. If your period consistently lasts longer than 7 days, or you experience very heavy bleeding (such as soaking through a pad or tampon in less than 2 hours), it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider.
How to Know If Your Periods Are Irregular?
While slight variations are normal, the following signs may indicate irregular periods:
- Cycles that are shorter than 21 or longer than 35 days
- Cycle length that varies significantly (e.g., 28 days, then 37, then 29)
- Skipping periods without pregnancy
- Excessively heavy bleeding (such as soaking through a pad or tampon in under an hour)
About 14% to 25% of women experience irregular cycles, often due to stress, weight changes, or conditions like PCOS. If irregularities persist, it’s wise to consult a healthcare provider.
Why Is My Period Irregular?
There are many reasons why periods can be irregular. Occasional changes are normal and may be caused by stress, travel, changes in weight, illness, or hormonal fluctuations. However, persistent irregularity, such as skipping periods or significant changes in cycle length, may be related to conditions like PCOS, thyroid issues, or other reproductive health concerns. If irregularity continues for several months, seek medical advice.
What Are Common Menstrual Symptoms to Expect?
Typical symptoms that may occur during different phases of your cycle include:
- Menstrual Cramps (Dysmenorrhea): Most people experience mild to moderate cramps, while about 5–15% endure severe discomfort that interferes with daily life. Heat therapy and over-the-counter medications often help. Persistent or intense pain warrants medical attention.
- Fatigue: Hormonal changes and blood loss may cause tiredness. In some cases, iron deficiency contributes to fatigue.
- Bloating: Temporary bloating is common due to hormonal shifts. If it persists longer than two weeks, seek medical advice.
- Mood Swings: Irritability, sadness, or emotional sensitivity can result from hormonal fluctuations. Self-care, exercise, and good sleep can help manage mood changes.
- Acne Breakouts: Hormonal irregularity during your cycle may trigger increased oil production, leading to acne.
- Breast Tenderness: Soreness or swelling is common before menstruation or around ovulation due to hormonal shifts.
Note: Severe or persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Can I Get Pregnant During My Period?
Although it’s less likely, it is still possible to get pregnant during your period. Sperm can live inside the body for up to 5 days, and if you ovulate early in your cycle, fertilization may occur. This is especially true for people with shorter cycles. Using contraception is recommended if you want to avoid pregnancy, regardless of where you are in your cycle.
What Causes Menstrual Cramps and How Can I Relieve Them?
Menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) are caused by uterine contractions that help shed the uterine lining. These contractions are triggered by hormone-like substances called prostaglandins. Mild cramps are common, but severe pain may indicate conditions like endometriosis or fibroids. Relief options include heating pads, gentle exercise, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen. If pain disrupts daily life, consult a healthcare provider.
When Should I See a Doctor About My Period?
You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Very heavy bleeding (changing pads/tampons every hour)
- Periods that last longer than 7 days
- Severe pain or cramping that doesn’t improve with medication
- Cycles shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days
- Missed periods for more than three months (and not pregnant)
These symptoms may signal underlying conditions such as PCOS, fibroids, thyroid disorders, or hormonal imbalances. Early evaluation can help with diagnosis and treatment.
What is a Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a monthly process that prepares the female body for potential pregnancy. It begins at puberty and continues until menopause, with an average cycle length of 28 days, though variations are normal.
How the Menstrual Cycle Works
The cycle starts on the first day of your period and ends the day before your next period begins. Hormones regulate each phase of the cycle, which includes:
- Uterine lining thickening to support a possible pregnancy
- Ovulation: the release of an egg around mid-cycle (typically day 14 in a 28-day cycle)
- Menstruation: the shedding of the uterine lining if pregnancy doesn’t occur
A cycle is considered regular if the difference between the shortest and longest cycles is less than 8 days.
What Is a Period?
Menstruation is the monthly shedding of the uterine lining, resulting in vaginal bleeding. This:
- Lasts between 2 to 7 days
- Marks the start of a new cycle (Day 1)
- Typically pauses during pregnancy and early breastfeeding
- Stops permanently at menopause (commonly between ages 49–52)